It might be sufficient to cover 1.5–2.7 meters of water on Mars.
When it was first discovered, Mars was a rust-colored ball of dust. However, this was not always the case. Mars had a climate similar to that of the primordial Earth, that is, it was moist and temperate billions of years ago. The European Space Agency (ESA) claims that it may have discovered the greatest storage of water ice on Mars to date. Scientists have discovered some of the water that has been missing from the planet due to its location around the planet. It would appear that a region close to the equator of Mars is home to enormous ice deposits that stretch more than two miles below the surface.
The Mars Express orbiter is responsible for the new analysis that has been conducted. Since its launch fifteen years ago, this spacecraft has been doing research on Mars, including a comprehensive investigation of a location in the equatorial region known as Medusae Fossae (shown above). During the time that Mars had active volcanoes, this collection of deep valleys and soaring ridges was most likely formed by a catastrophic volcanic event with the help of a volcanic eruption. There is a possibility that the eroding surface features of the Medusae Fossae are the origin of practically all of the dust that is found on Mars. According to the European Space Agency (ESA), it is also possible that it is the location of practically all of Mars’ water that has been gone.
When Mars Express first began its investigation of the Medusae Fossae, the crew discovered pockets of a material that had a lower density than the rock that was all around it. However, it was not apparent what the lower density material was. The new information obtained from the Radar for Subsurface and Ionospheric Sounding (MARSIS) instrument aboard the Mars Express indicates that Medusae Fossae may be the location of subsurface blocks of water ice that stretch many miles below the surface from the surface.
In the past, scientists were cautious in their assertion that Medusae Fossae contained water ice; nonetheless, there were other conceivable reasons for the low density of Medusae Fossae. One possible explanation for the deposits is that they were composed of compressed dust or volcanic ash. The ice hypothesis, on the other hand, is supported by the revised MARSIS radar data. As part of their efforts to provide an explanation for what they observed, the team evaluated the most recent radar pictures and developed models. There was not a single ice-free substance that could explain the findings.
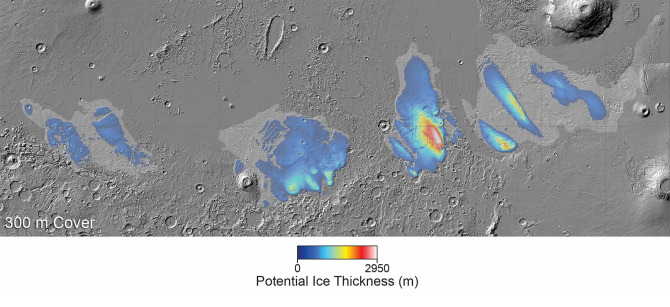
“If [Medusae Fossae] was simply a giant pile of dust, we would expect it to become compacted under its own weight,” explains Andrea Cicchetti, who is a co-author of the study and works at the National Institute for Astrophysics in Italy. “This would create something far denser than what we actually see with MARSIS.”
According to the calculations made by the scientists, the thickness of the ice layers might reach up to 2.3 miles (about 3.7 kilometers). In the event that it melted, it would be sufficient to cover the entire surface of Mars with water that is between 1.5 and 2.7 meters deep. The volume of that is roughly equivalent to that of the Red Sea on Earth. This discovery has the potential to not only influence our understanding of the geological history of Mars, but it also has the potential to open up new avenues for long-term research. It would be beneficial for both robotic and crewed exploration to have access to water once it is discovered on Mars.
Unfortunately, given the current state of technology, it is highly unlikely that this water can be accessed. Deep mining on another planet is still the stuff of science fiction, and the ice is shielded from the elements by several hundred meters of dust. On the other hand, there is a possibility that Medusae Fossae will become the first watering hole on Mars when the time comes when it is not.

