AlphaFold 3 builds on earlier versions of the software that have already mapped out more than 200 million proteins.
Recent artificial intelligence (AI) hype has focused a significant portion of its attention on the fascinating digital material that can be generated from simple prompts. Additionally, there have been concerns regarding the capability of AI to decimate the workforce and make malevolent propaganda far more persuasive. (What a blast!) However, some of the most intriguing (and perhaps much less frightening) work that artificial intelligence can do is in the medical field. It is possible that a recent update to the AlphaFold software developed by Google will result in new discoveries about disease study and treatment.
The AlphaFold software, which was developed by Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs, which is also owned by Alphabet, has already proved that it is capable of accurately predicting how proteins fold thanks to its remarkable precision. The database has an astounding 200 million proteins that are known to exist, and according to Google, millions of researchers have used earlier versions of the database to produce breakthroughs in fields such as the development of enzymes, cancer treatments, and vaccines against malaria.
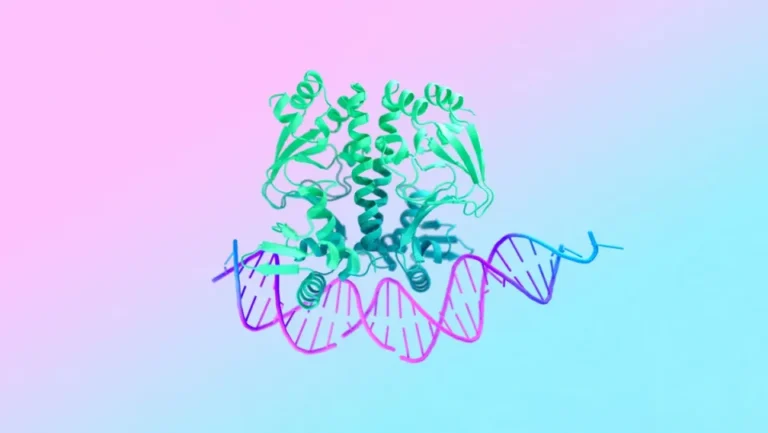
By gaining an understanding of the shape and structure of a protein, scientists are able to establish how it interacts with the human body. This enables them to develop new medications or improve those that already exist. On the other hand, the most recent version, AlphaFold 3, is capable of modeling other essential molecules, such as DNA. In addition to this, it is able to monitor interactions between diseases and medications, which may provide researchers with fascinating new avenues to explore. And Google claims that it is able to do so with an accuracy that is fifty percent higher than earlier models.
According to a blog post written by the DeepMind research team at Google, “AlphaFold 3 takes us beyond proteins to a broad spectrum of biomolecules.” This breakthrough could enable further disruptive science, including the development of biorenewable materials and crops that are more resistant to harsh conditions, as well as the acceleration of research on medicine design and genetics.
What are the mechanisms by which proteins react to DNA damage, and how do they locate and repair it? Wired was informed by John Jumper, the leader of the Google DeepMind research. “It is possible for us to begin answering these questions.”
Before the advent of artificial intelligence, the only way for scientists to investigate the structures of proteins was through the use of electron microscopes and other complex techniques such as X-ray crystallography. By utilizing patterns that are recognized from its training (which are frequently invisible to humans and our normal tools), machine learning streamlines a significant portion of that process. This is accomplished by predicting protein shapes based on the amino acids that they contain.
Google claims that the application of diffusion models to its molecular predictions is responsible for a portion of the gains made by AlphaFold 3. Artificial intelligence image generators such as Midjourney, Google’s Gemini, and OpenAI’s DALL-E 3 all rely heavily on diffusion models as its core components. As explained by Wired, the incorporation of these algorithms into AlphaFold “sharpens the molecular structures that the software generates.” To put it another way, it takes a configuration that appears hazy or ambiguous and then uses highly educated predictions based on patterns from its training data in order to clarify it.
In an interview with Wired, Demis Hassabis, CEO of Google DeepMind, stated that “this is a big advance for us.” “This is exactly what you need for drug discovery: You need to see how a small molecule is going to bind to a drug, how strongly it is going to bind, and also what else it might bind to,”
Using a color-coded scale, AlphaFold 3 labels the level of confidence it has in its prediction. This enables researchers to exercise appropriate caution when dealing with results that are less likely to be true. The color blue indicates a high level of confidence, while the color red indicates a lower level of certainty.
Researchers will be able to use AlphaFold 3 for free for research that is not for commercial gain thanks to Google. On the other hand, in contrast to previous iterations, the corporation is not engaging in open-sourcing the project. One of the most notable researchers who creates software that is comparable, David Baker, a professor at the University of Washington, stated his dissatisfaction to Wired regarding Google’s decision to go there. Having said that, he was even more impressed with the possibilities of the software. It was noted by him that the performance of AlphaFold 3 in terms of structure prediction is really impressive.
Google has stated that “Isomorphic Labs is already collaborating with pharmaceutical companies to apply it to real-world drug design challenges and, ultimately, develop new life-changing treatments for patients.” This is in reference to the upcoming developments.